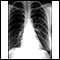
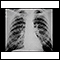
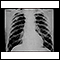
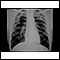
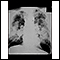
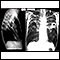
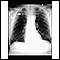
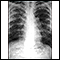
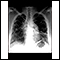
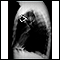
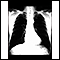
Chest x-ray
Definition
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
Alternative Names
Chest radiography; Serial chest x-ray; X-ray - chest
How the Test is Performed
You stand in front of the x-ray machine. You will be told to hold your breath when the x-ray is taken.
Two images are usually taken. You will first need to stand facing the machine, and then sideways.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell the health care provider if you are pregnant. Chest x-rays are generally not done during pregnancy, and special precautions are taken if they are needed.
How the Test will Feel
There is no discomfort. The imaging plate may feel cold.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may order a chest x-ray if you have any of the following symptoms:
- A persistent cough
- Chest pain from a chest injury (with a possible rib fracture or lung complication) or from heart problems
- Coughing up blood
- Difficulty breathing
- Fever
It may also be done if you have signs of tuberculosis, lung cancer, or other chest or lung diseases.
A serial chest x-ray is one that is repeated. It may be done to monitor changes found on a past chest x-ray.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to many things, including:
In the lungs:
- Collapsed lung
- Collection of fluid around the lung
- Lung tumor (noncancerous or cancerous)
- Malformation of the blood vessels
- Pneumonia
- Scarring of lung tissue
- Tuberculosis
- Atelectasis
In the heart:
- Problems with the size, position or shape of the heart
- Problems with the position, size and shape of the large arteries
- Evidence of heart failure
In the bones:
- Fractures or other problems of the ribs and spine
- Osteoporosis
In the mediastinum (middle part of the chest):
- Enlargement, which might be related to infection or tumor
Risks
There is low radiation exposure. X-rays are monitored and regulated to provide the minimum amount of radiation exposure needed to produce the image. Most experts feel that the benefits outweigh the risks. Pregnant women and children are more sensitive to the risks of x-rays.
References
Chernecky CC, Berger BJ. Chest radiography (chest x-ray, CXR) - diagnostic norm. In: Chernecky CC, Berger BJ, eds. Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:327-328.
Felker GM, Teerlink JR. Diagnosis and management of acute heart failure. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 49.
Jokerst CE, Gotway MB. Thoracic radiology: noninvasive diagnostic imaging. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 20.
Review Date:7/31/2022
Reviewed By:Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron, Jr. Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.

Health Outcome Data
No data available for this condition/procedure.
Read More
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease
Cerebral arteriovenous malformation
Collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
Community-acquired pneumonia in adults
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus
Drug-induced pulmonary disease
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Histoplasmosis - acute (primary) pulmonary
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
Pericarditis - after heart attack
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
Pneumonia - weakened immune system
Primary alveolar hypoventilation
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
Transposition of the great arteries