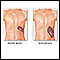
Splenomegaly
Definition
Splenomegaly is a larger-than-normal spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left part of the belly.
Alternative Names
Spleen enlargement; Enlarged spleen; Spleen swelling
Considerations
The spleen is an organ that is a part of the lymph system. The spleen filters the blood and maintains healthy red and white blood cells and platelets. It also plays a role in immune function.
Many health conditions can affect the spleen. These include:
- Diseases of the blood or lymph system
- Infections
- Cancer
- Liver disease
Symptoms of splenomegaly include:
- Hiccups
- Inability to eat a large meal
- Pain in the upper left side of the belly
Causes
Splenomegaly can be caused by any of the following:
- Infections
- Liver diseases
- Blood diseases
- Cancer
Home Care
In rare cases, an injury can rupture the spleen. If you have splenomegaly, your health care provider may advise you to avoid contact sports. Your provider will tell you what else you need to do to take care of yourself and any medical condition.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
There are usually no symptoms from an enlarged spleen. Seek medical help right away if pain in your belly is severe or gets worse when you take a deep breath.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history.
A physical exam will be done. The provider will feel and tap along the upper left part of your belly, especially just under the rib cage.
Tests that may be done include:
- Abdominal x-ray, ultrasound, or CT scan
- Blood tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) and tests of your liver function
Treatment depends on the cause of splenomegaly.
References
Vos PM, Barnard SA, Cooperberg PL. Benign and malignant lesions of the spleen. In: Gore RM, Levine MS, eds. Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 105.
Vos PM, Mathieson JR, Cooperberg PL. The spleen. In: Rumack CM, Levine D, eds. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 5.
Winter JN. Approach to the patient with lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 159.
Review Date:1/25/2022
Reviewed By:Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.