Swollen lymph nodes
Definition
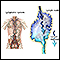
Lymph nodes are present throughout your body. They are an important part of your immune system. Lymph nodes help your body recognize and fight germs, infections, and other foreign substances.
The term "swollen glands" refers to enlargement of one or more lymph nodes. The medical name for swollen lymph nodes is lymphadenopathy.
In a child, a node is considered enlarged if it is more than 1 centimeter (0.4 inch) wide.
Alternative Names
Swollen glands; Glands - swollen; Lymph nodes - swollen; Lymphadenopathy
Considerations
|
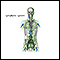
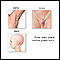
Common areas where the lymph nodes can be felt (with the fingers) include:
- Groin
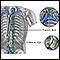
- Armpit
- Neck (there is a chain of lymph nodes on either side of the front of the neck, both sides of the neck, and down each side of the back of the neck)
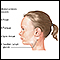
- Under the jaw and chin
- Behind the ears
- On the back of the head
Causes
Infections are the most common cause of swollen lymph nodes. Infections that can cause them include:
- Abscessed or impacted tooth
- Ear infection
- Colds, flu, and other infections
- Swelling (inflammation) of gums (gingivitis)
- Mononucleosis
- Mouth sores
- Sexually transmitted illness (STI)
- Tonsillitis
- Tuberculosis
- Skin infections
Immune or autoimmune disorders that can cause swollen lymph nodes are:
- HIV
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Cancers that can cause swollen lymph nodes include:
Many other cancers may also cause this problem.
Certain medicines can cause swollen lymph nodes, including:
- Seizure medicines, such as phenytoin
- Typhoid immunization
Which lymph nodes are swollen depends on the cause and the body parts involved. Swollen lymph nodes that appear suddenly and are painful are usually due to injury or infection. Slow, painless swelling may be due to cancer or a tumor.
Home Care
Painful lymph nodes are generally a sign that your body is fighting an infection. The soreness usually goes away in a couple of days without treatment. The lymph node may not return to its normal size for several weeks.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- Your lymph nodes do not get smaller after several weeks or they continue to get larger.
- They are red and tender.
- They feel hard, irregular, or fixed in place.
- You have fever, night sweats, or unexplained weight loss.
- Any node in a child is larger than 1 centimeter (a little less than half inch) in diameter.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical examination and ask about your medical history and symptoms. Examples of questions that may be asked include:
- When the swelling began
- If the swelling came on suddenly
- Whether any nodes are painful when pressed
The following tests may be done:
- Blood tests, including liver function tests, kidney function tests, and CBC with differential
- Lymph node biopsy
- Chest x-ray
- Liver-spleen scan
Treatment depends on the cause of the swollen nodes.
References
Tower RL, Camitta BM. Lymphadenopathy. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 517.
Winter JN. Approach to the patient with lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 159.
Review Date:1/29/2022
Reviewed By:Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.