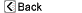Pancreatitis
Normal anatomy
|
|
The pancreas is located in the upper part of the abdomen, behind the stomach. It contains cells that secrete the hormone insulin, and cells that secrete digestive enzymes that aid in the breakdown of food in the gastrointestinal tract. The pancreas secretes these enzymes into the pancreatic duct, which joins the common bile duct from the liver and drains into the small intestine.
|
Indication
|
|
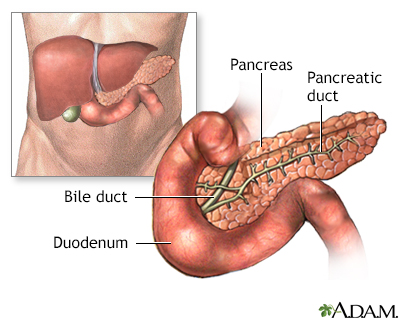
Inflammation of the pancreas, or pancreatitis, is a serious condition that is most commonly caused by either alcohol toxicity or gallstones.
Gallstones can lodge in the common bile duct and block the flow of pancreatic enzymes out of the pancreas into the intestine.
Pancreatitis due to alcohol toxicity is most often seen in chronic alcoholic patients. Most often, pancreatitis goes away with nonsurgical therapy. The patient will not be allowed to eat for three to five days, to prevent secretion of enzymes by the pancreas. He will also receive pain medication to control the pain caused by pancreatic inflammation.
|
Procedure
|
|
If pancreatitis is due to gallstones, most often the responsible gallstone passes into the intestine spontaneously, and the pancreatitis goes away.
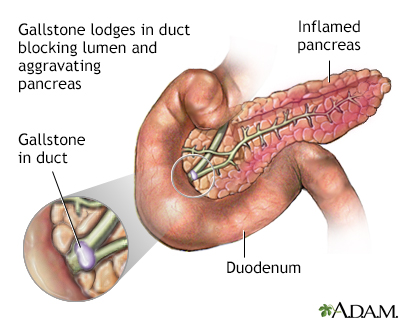
Less commonly, a minor surgical procedure is necessary to extract a gallstone that is blocking the pancreatic duct where it drains into the small intestine. An endoscope, with a camera on its end, is passed down the esophagus, through the stomach, and into the small intestine. The entrance of the pancreatic duct into the small intestine can be viewed through the endoscope. A special instrument on the end of the endoscope can then be passed into the pancreatic duct and the gallstone is extracted.
Very rarely pancreatitis is severe enough to require surgery, which is usually performed when the pancreas becomes infected. Dead pancreatic tissue is removed, and the area around the pancreas is washed clean. Patients who require such treatment usually have prolonged hospital stays and are seriously ill.
|
Review Date:10/26/2021
Reviewed By:Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency
or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional
should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911
for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they
do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.