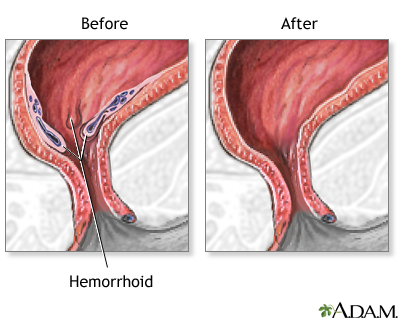
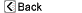Hemorrhoid surgery
Normal anatomy
|
|
The rectum is the final portion of the large intestine. It empties stool from the body through the anus. Hemorrhoids are "cushions" of tissue filled with blood vessels at the junction of the rectum and the anus.
|
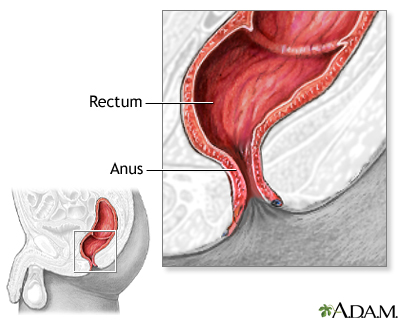
Indications
|
|
These vascular cushions can become swollen and inflamed, usually due to increased intra-abdominal pressure, such as during straining when constipated or during pregnancy. Such swelling can cause pain, bleeding, and itching. Hemorrhoid removal may be recommended when non-surgical treatment (fiber rich diet, laxatives, stool softener, suppositories, medications, warm baths) has not provided adequate relief from:
- Persistent itching
- Anal bleeding
- Pain
- Blood clots (thrombosis of the hemorrhoids)
|
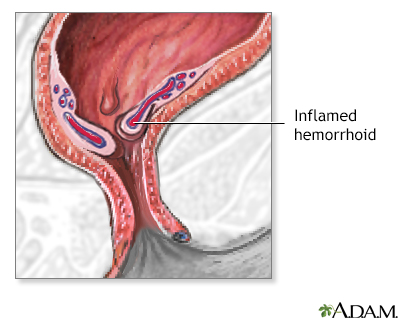
Procedure
|
|
The hemorrhoid is ligated at its base, to prevent bleeding from the blood vessels within the hemorrhoid, then it is removed surgically. Alternatively, some surgeons will simply apply a rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid (banding); deprived of its blood supply, the hemorrhoid will then simply fall off and be passed in the stool. Finally, some surgeons will inject the base of the hemorrhoid with a sclerosing agent (sclerotherapy), which also destroys the vessels in the hemorrhoid, causing it to fall off and be passed in the stool.
|
Aftercare
|
|
The outcome is very good in more than 90% of the cases. The patient may experience considerable pain after surgery as the anus tightens and relaxes. Medications to relieve pain may be used. To avoid straining, stool softeners will be used. Avoid any straining during bowel movement or urination. Soaking in a warm bath can bring additional comfort. Expect complete recovery in about 2 weeks.
|
Review Date:9/9/2023
Reviewed By:Debra G. Wechter, MD, FACS, General Surgery Practice Specializing in Breast Cancer, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency
or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional
should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911
for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they
do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.