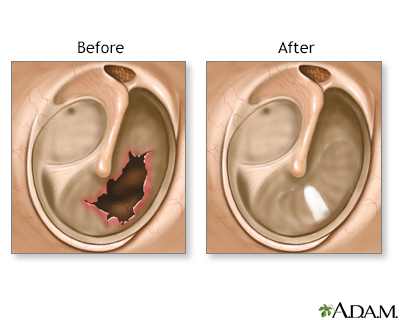
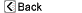Eardrum repair
Normal anatomy
|
|
The tympanic membrane (eardrum) separates the outer ear from the middle ear. The membrane vibrates when sound waves strike it, beginning the process that converts the sound wave into a nerve impulse that travels to the brain.
|
Indication
|
|
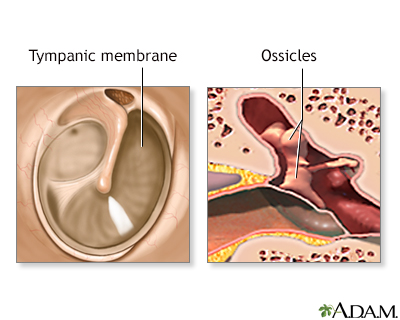
Ruptured or perforated eardrums are usually caused by middle-ear infections or trauma (for example, an object in the ear, a slap on the ear, explosions, or repeated, excessive ear pressure from flying or diving).
If healing does not occur with antibiotics or other non-operative treatment, surgery may be necessary.
Chronic middle ear infections are described as:
- 5 or more ear infections in a year, or
- 3 or more ear infections a year over a two-year period
Signs of chronic ear infections include persistent ear pain, ear drainage, or hearing loss (over a 3-month period).
|
Procedure
|
|
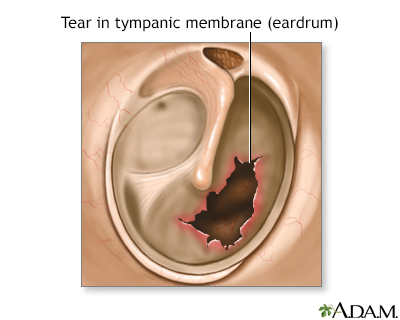
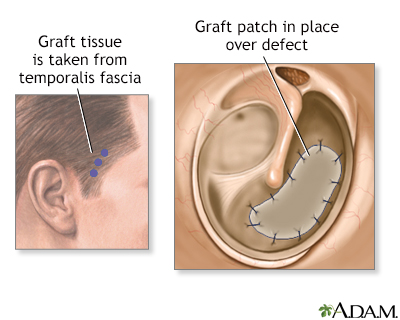
While the patient is deep asleep and pain-free, (general anesthesia), the surgeon grafts a small patch from the fascia of the forehead muscle (temporalis) onto the eardrum. This graft is used to repair the tear.
For problems with the small bones (ossicles), the surgeon will use an operating microscope to view and repair the chain of small bones using plastic devices or ossicles from a donor.
|
Aftercare
|
|
In most cases, the operation relieves pain and infection symptoms completely. Hearing loss is usually minor. However, if the ossicles require repair, outcome may be less optimal.
Patients usually leave the hospital the same day. After surgery, it is important to avoid getting water in the ear. Use a hair cap when showering for a few weeks.
|
Review Date:5/30/2022
Reviewed By:Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency
or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional
should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911
for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they
do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.