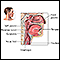
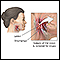
Oropharynx lesion biopsy
Definition
An oropharynx lesion biopsy is surgery in which tissue from an abnormal growth or mouth sore is removed and checked for disease.
Alternative Names
Throat lesion biopsy; Biopsy - mouth or throat; Mouth lesion biopsy; Oral cancer - biopsy
How the Test is Performed
Painkilling or numbing medicine is first applied to the area. For large sores or sores of the throat, general anesthesia may be needed. This means you will be asleep during the procedure.
All or part of the problem area (lesion) is removed. It is sent to the laboratory to check for diseases. If a growth in the mouth or throat needs to be removed, the biopsy will be done first. This is followed by the actual removal of the growth.
How to Prepare for the Test
If a simple painkilling or local numbing medicine is to be used, there is no special preparation. If the test is part of a growth removal or if general anesthesia is used, you will likely be asked not to eat for 6 to 8 hours before the test.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel pressure or tugging while the tissue is being removed. After the numbness wears off, the area may be sore for a few days.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to determine the cause of a sore (lesion) in the throat.
Normal Results
This test is only done when there is an abnormal tissue area.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may mean:
- Cancer (such as squamous cell carcinoma)
- Benign lesions (such as papilloma)
- Fungal infections (such as candida)
- Histoplasmosis
- Oral lichen planus
- Precancerous sore (leukoplakia)
- Viral infections (such as Herpes simplex)
Risks
Risks of the procedure may include:
- Infection of the site
- Bleeding at the site
If there is bleeding, the blood vessels may be sealed (cauterized) with an electric current or laser.
Considerations
Avoid hot or spicy food after the biopsy.
References
Dockrell DH, Ho A, Gordon SB. Community-acquired pneumonia. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 46.
Sinha P, Harréus U. Malignant neoplasms of the oropharynx. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 96.
Review Date:11/29/2022
Reviewed By:Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.