Amniotic fluid
Definition
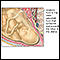
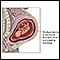
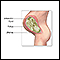
Amniotic fluid is a clear, slightly yellowish liquid that surrounds the unborn baby (fetus) during pregnancy. It is contained in the amniotic sac.
Information
While in the womb, the baby floats in the amniotic fluid. The amount of amniotic fluid is greatest at about 34 weeks into the pregnancy (34 weeks gestation), when it averages 800 mL. About 600 mL of amniotic fluid surrounds the baby at full term (40 weeks gestation).
The amniotic fluid constantly moves (circulates) as the baby swallows and "inhales" the fluid, and then releases it.
The amniotic fluid helps:
- The developing baby to move in the womb, which allows for proper bone growth
- The lungs to develop properly
- Prevent pressure on the umbilical cord
- Keep a constant temperature around the baby, protecting from heat loss
- Protect the baby from outside injury by cushioning sudden blows or movements
Too much amniotic fluid is called polyhydramnios. This condition can occur with multiple pregnancies (twins or triplets), congenital anomalies (problems that exist when the baby is born), or gestational diabetes.
Too little amniotic fluid is known as oligohydramnios. This condition may occur with late pregnancies, ruptured membranes, placental dysfunction, or fetal abnormalities.
Abnormal amounts of amniotic fluid may cause the health care provider to watch the pregnancy more carefully. Removing a sample of the fluid through amniocentesis can provide information about the sex, health, and development of the fetus.
References
Burton GJ, Sibley CP, Jauniaux ERM. Placental anatomy and physiology. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 1.
Gilbert WM. Amniotic fluid disorders. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 28.
Ross MG, Beall MH. Amniotic fluid dynamics. In: Lockwood CJ, Copel JA, Dugoff L, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 4.
Review Date:11/10/2022
Reviewed By:John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.