Cervical polyps
Definition
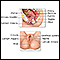
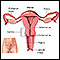
Cervical polyps are fingerlike growths on the lower part of the uterus that connects with the vagina (cervix).
Alternative Names
Vaginal bleeding - polyps
Causes
The exact cause of cervical polyps is not known. They may occur with:
- An abnormal response to increased levels of the female hormone estrogen
- Chronic inflammation
- Clogged blood vessels in the cervix
Cervical polyps are common. They are often found in women over age 40 who have had many children. Polyps are rare in young women who have not started having their period (menstruation).
Symptoms
Polyps do not always cause symptoms. When symptoms are present, they may include:
- Very heavy menstrual periods
- Vaginal bleeding after douching or intercourse
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding after menopause or between periods
- White or yellow mucus (leukorrhea)
Exams and Tests
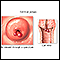
Your health care provider will perform a pelvic exam. Some smooth, red or purple fingerlike growths will be seen on the cervix.
Most often, the provider will remove the polyp with a gentle tug and send it for testing. Most of the time, the biopsy will show cells that are consistent with a benign polyp. Rarely, there may be abnormal, precancerous, or cancer cells in a polyp.
Treatment
The provider can remove polyps during a simple outpatient procedure.
- Smaller polyps may be removed with gentle twisting.
- Electrocautery may be needed to remove larger polyps.
The removed polyp tissue should be sent to a lab for further tests.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most polyps are not cancerous (benign) and are easy to remove. Polyps do not grow back most of the time. Women who have polyps are at risk of growing more polyps.
Possible Complications
There may be bleeding and slight cramping for a few days after removal of a polyp. Some cervical cancers may first appear as a polyp. Certain uterine polyps may be associated with uterine cancer.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have:
- Abnormal bleeding from the vagina, including bleeding after sex or between periods
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina
- Abnormally heavy periods
- Bleeding or spotting after menopause
Contact your provider to schedule regular gynecological exams. Ask how often you should receive a Pap test.
Prevention
See your provider to treat infections as soon as possible.
References
Choby BA. Cervical polyps. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 123.
Dolan MS, Hill CC, Valea FA. Benign gynecologic lesions: vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, oviduct, ovary, ultrasound imaging of pelvic structures. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 18.
Review Date:1/10/2022
Reviewed By:John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.